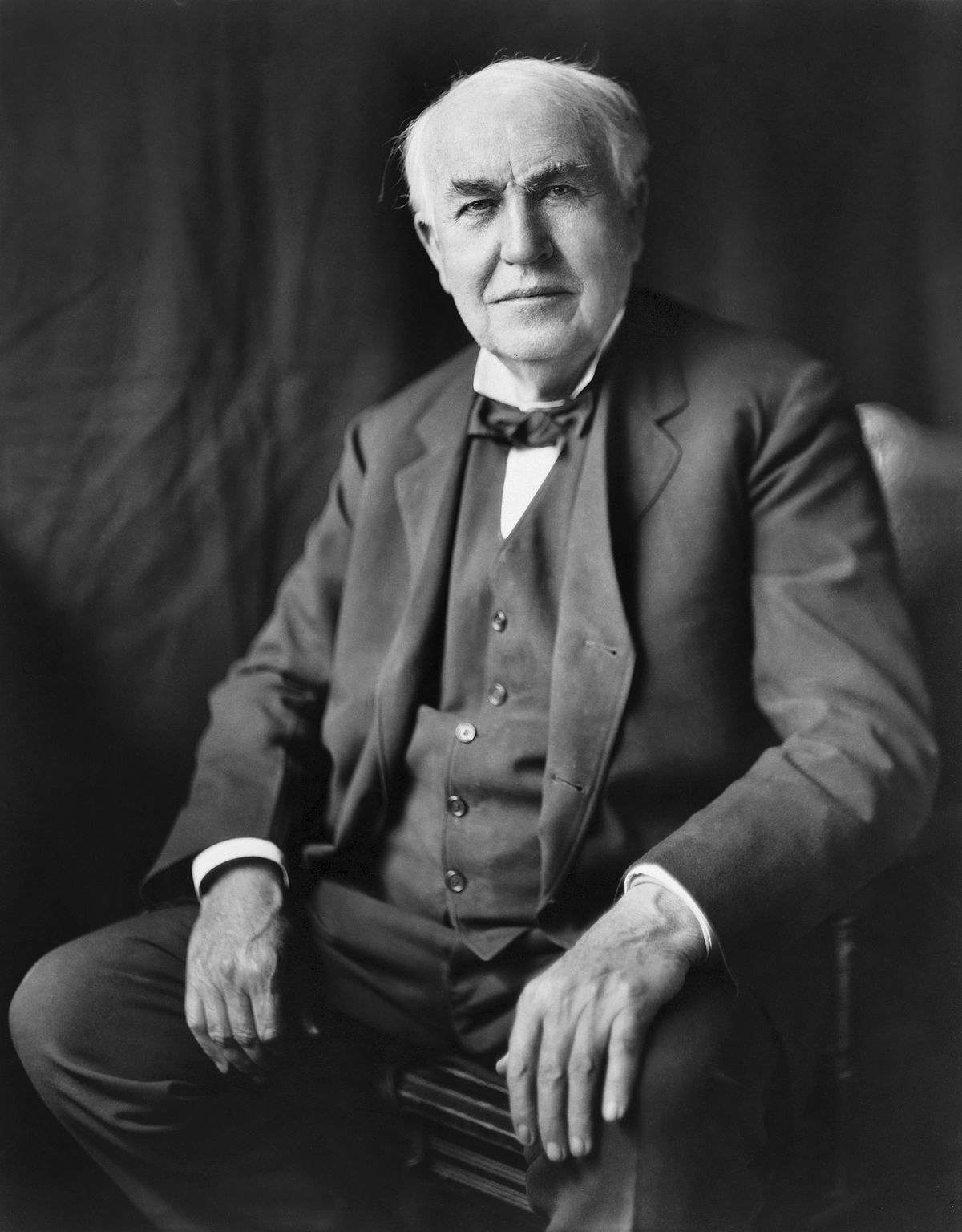
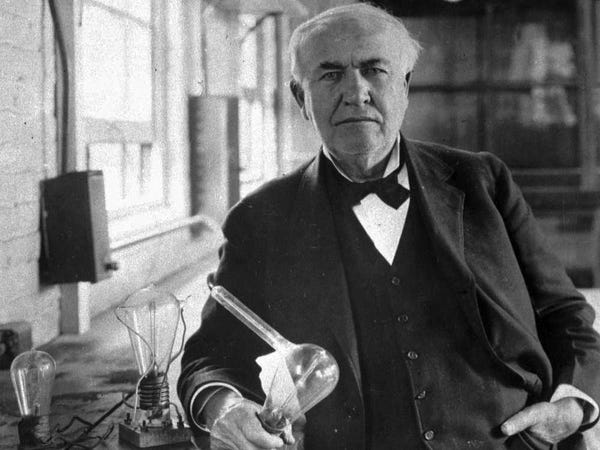
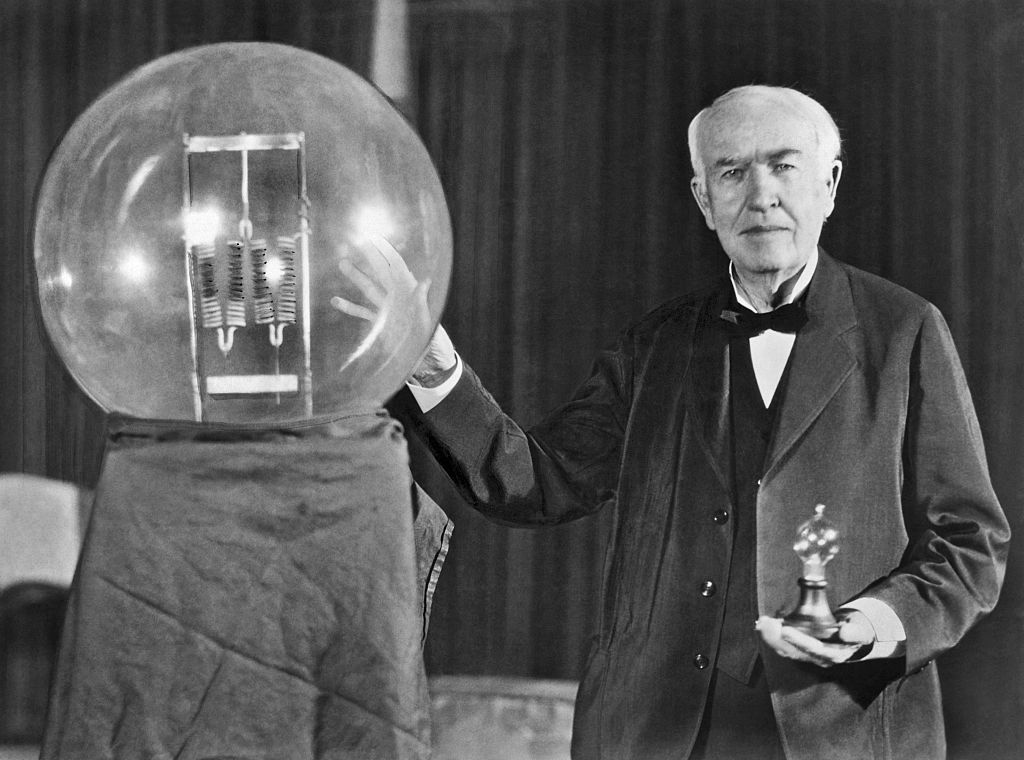
Early Life
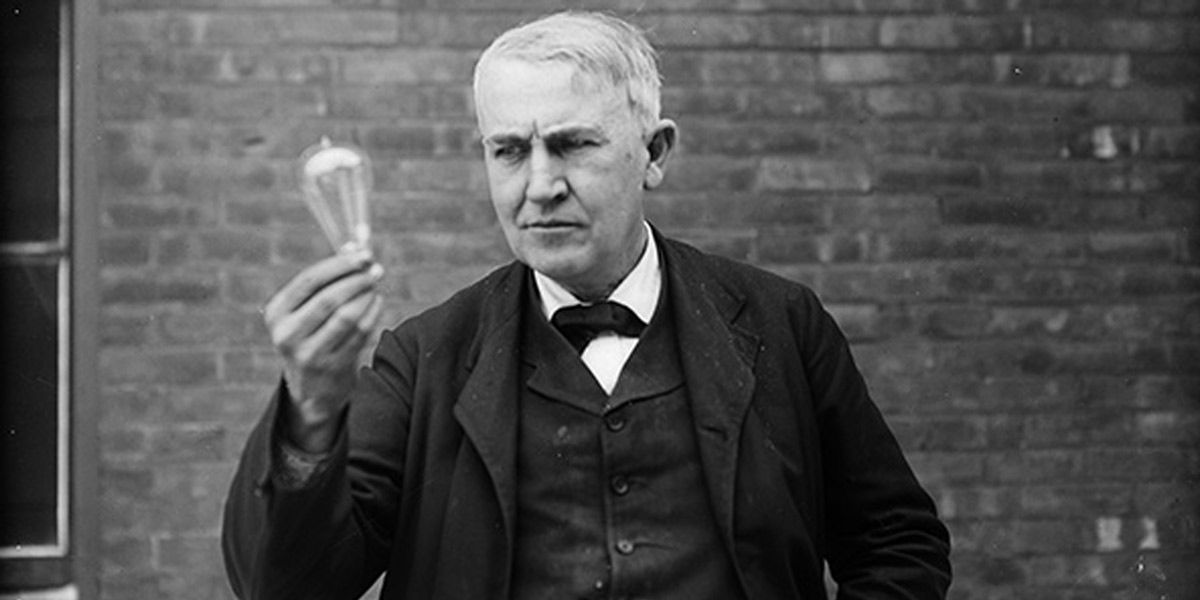
Thomas Alva Edison, born in Ohio on February 11, 1847, was one of the most well-known inventors of all time. He spent a few of his early years in formal schooling, but he received most of his education at home. Thomas set up a laboratory in the basement of his family's Michigan home and spent most of his time experimenting.Edison developed hearing problems at the age of 12. The cause of his deafness has been attributed to a bout of scarlet fever during childhood and recurring untreated middle-ear infections. He subsequently concocted elaborate fictitious stories about the cause of his deafness. As he was completely deaf in one ear and barely hearing in the other, it is alleged that Edison would listen to a music player or piano by clamping his teeth into the wood to absorb the sound waves into his skull. As he got older, Edison believed his hearing loss allowed him to avoid distraction and concentrate more easily on his work.